The state agency responsible for ensuring Uber and Lyft rides are safe failed to consistently track the number of accidents, assaults and drunk driving complaints that occur on them, according to a new study by San Francisco traffic planners.
The California Public Utilities Commission did not even consistently collect the most basic industry information, such as ride requests and miles driven, the report from the San Francisco County Transportation Authority shows.
The state’s spotty information about company operations makes it more difficult for policy makers, especially at the local level, to address top priorities like road safety, air quality and access to transportation for people with disabilities, the study says.
Cities bear the brunt of congestion and other industry side effects — particularly San Francisco, which had by far the greatest ride concentration of any municipality in the state, with more than 820,000 trips per square mile in the year ending Aug. 30, 2020. But they have little jurisdiction over the ride-hailing giants, which are regulated by the state.
“The lack of accurate, timely and transparent data has left localities without necessary information to support a basic understanding” of ride-hailing company operations within their borders, the study said.
According to the report, the commission let Uber and Lyft submit inconsistent and incomplete data in their mandatory annual reports to the agency.
The problems are exacerbated “if not directly caused by” the commission’s unclear reporting requirements and “lack of quality assurance or enforcement of quality standards,” it said.
On Tuesday, Joe Castiglione, deputy director for technology, data and analysis at the Transportation Authority, presented the study to its board.
“TNC 2020: A Profile of Ride-Hailing in California,” is the first broad analysis of annual reports from Uber and Lyft, which are the dominant players in a sector known as transportation network companies. It covers September 2019 to August 2020, the interval for which the most complete data is available.
Although the transportation agency’s initial goal was to examine ride-hailing’s effects on the state’s people and environment, it also found “pervasive” problems with the commission’s data collection practices.
Among the study’s findings:
- Lyft filed only 36% of the required data with the commission, while Uber reported more than 99%, suggesting that the commission enforced the reporting rules inconsistently.
- Even basic data on company activity was self-contradictory, with Lyft stating two different figures for its total completed trips that varied by 49.7 million trips, or 81%. Uber’s totals varied by 9.3 million trips, or 6%.
- If San Francisco had accurate figures, Castiglione told the board, it could better assess whether Uber and Lyft are paying the city a per-trip surcharge that funds public transportation.
- Uber produced an estimated 494,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide, an amount comparable to that released by the 2020 Caldwell Fire in Northern California, which burned 81,000 acres. Almost a third of those vehicle emissions occurred with no passengers aboard. Because Lyft’s mileage data was incomplete, its emissions could not be estimated.
- While ride-hailing companies promised to reduce congestion through shared travel, the data shows that just 14% of calls are for “pooled” rides, and only 7% are filled.
- Only about half of all requests for wheelchair-accessible vehicles were served. Uber completed 47%, and Lyft 53%.
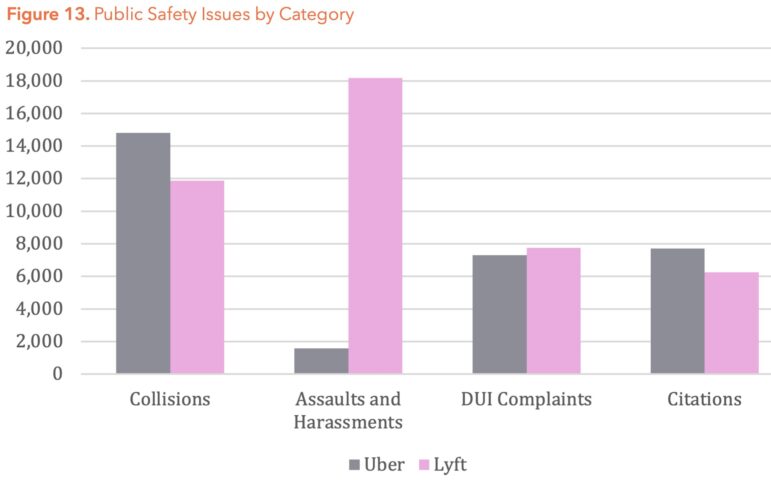
- Lyft reported three times as many public safety incidents on a per-trip basis as Uber did. These include collisions, assaults, harassments, drunk driving complaints and traffic citations. Lyft reported 30 times as many assaults and harassments as Uber did on a per-trip basis.
However, the study noted that the firms may be reporting differently, “pointing to the need for increased review by regulators.”
The ride-hailing firms have said that more than 99% of their trips end without safety issues, and that they have added security features to their apps. Uber, for example, offers “share my trip,” which lets riders send their location to friends or family. Lyft has a similar option.
San Francisco County Transportation Authority
Lyft reported three times more incidents per trip than the much larger Uber in the year ending Aug. 30, 2020, suggesting inconsistent data collection. Total counts of each category — Collisions: Uber, 14,805; Lyft, 11,877. Assaults and harassment: Uber, 1,573; Lyft, 18,178. Drunk driving complaints: Uber, 7,294; Lyft, 7,745. Traffic citations: Uber, 7,711; Lyft, 6,259. Sources: SFCTA public information office, and report, “TNC 2020,” page 41.The state commission has also released the firms’ 2021 data filings, but the local study said they appeared to be even less complete, and so heavily redacted they could not be fully evaluated.
The Transportation Authority emphasized that the commission, which also regulates driverless vehicles across California, has been heavily redacting its reports on them as well, even though cities need quality data on how the nascent services may affect them.
In 2013 the commission became the first agency in the nation to legalize ride-hailing, and is the only state agency that collects comprehensive data on the industry.
Terrie Prosper, the commission’s spokeswoman, said in an email that the agency was aware of the city’s concerns. “CPUC staff have been working with the TNCs to rectify many of the concerns for the 2020 data and for subsequent reporting years,” she said.
Uber and Lyft spokespeople said in emails Monday that they had complied with the commission’s requests for information, but questioned the study’s overall conclusions. They did not respond to questions about specific findings.
The commission’s faulty data collection came to light in October 2021, after the Public Press obtained data on assaults and harassments from the 2020 annual safety filings for Uber and Lyft under the California Public Records Act. It was the first public disclosure of any annual ride-hailing safety reports, revealing that numbers the firms submitted to the commission varied widely.
The commission confirmed in a ruling in January 2022 that it had let the ride-hailing giants use varying definitions of sexual assault since at least 2017, and this “could impact the total number and types of incidents reported in their annual reports.”
The commission in June 2022 voted to require uniform definitions in reporting assault complaints. It did not address other categories of data.

SFGovTV
Transportation Authority board member Dean Preston said Lyft and state regulators should be held accountable for not providing basic information.San Francisco Supervisor Dean Preston, one of several Transportation Authority board members, at the hearing Tuesday expressed frustration with the state commission.
“We basically privatized and deregulated transportation, and this is what we get: clogged street, no accountability, no data,” he said. “This is a joke. I mean, a cruel joke in terms of data integrity.”
Read more about the ride-hailing industry and the record of state regulators in our ongoing series, “Ride Hailing’s Dark Data.”









